This 17th episode is titled “What a Difference a Century Makes.”
During the mid-4th Century, the history of the Church walked apace with the history of the Roman Empire. With the death of Constantine the Great, the rule of the Empire divided among his 3 sons, Constantine II, Constans, & Constantius. In the power-hungry maneuverings that followed, they did their upbringing in a Christian education little honor. They quickly removed any challenge by their father’s relatives, then set to work on one another. 3 years after their father’s death they went to war in a struggle for sole supremacy. Constantine II was slain by Constans, who was in turn murdered by a Gallic commander of the Imperial guard named Magnentius. After the defeat and suicide of Magnentius, Constantius became sole Emperor & reigned till his death in 361.
Constantius departed from his father Constantine’s wise policy of religious toleration. Constantius was greatly influenced by the Arian bishop of Constantinople Eusebius who inspired him to use the authority of his office to enforce the Arian-brand of Christianity not only on the pagans of the Empire but also on those Christians who followed the Nicene Orthodoxy. Paganism was violently suppressed. Temples were pillaged and destroyed with the loot taken from them given either to the Church or Constantius’ supporters. As Christians had earlier been subject to arrest & execution, so now were pagans. Not unexpectedly, large numbers of former pagans came over to Christianity; their conversion feigned. A similar persecution was applied towards Nicaean Christians. They were punished with confiscation and banishment.
Constantius meddled in most of the Church’s affairs, which during his reign was fraught with doctrinal controversy. He called a multitude of councils; in Gaul, Italy, Illyricum, & Asia. He fancied himself an accomplished theologian and enjoyed being called Bishop of bishops.
Constantius justified his violent suppression of paganism by likening it to God’s command to Israel to wipe out the idol-worshipping Canaanites. But intelligent church leaders like Athanasius argued instead for toleration. Athanasius wrote,
Satan, because there is no truth in him, breaks in with ax and sword. But the Savior is gentle, and forces no one to whom He comes, but knocks on and speaks to the soul: ‘Open to me, my sister?’ If we open to Him He enters but if we will not, He departs. For the truth is not preached by sword and dungeon, by the might of an army, but by persuasion and exhortation. How can there be persuasion where the fear of the Emperor is uppermost? How exhortation, where the contradictory has to expect banishment and death?
The ever-swinging pendulum of history foretells that the forced-upon faith of Constantius will provoke a pagan reaction. That reaction came immediately after Constantius during the reign of his cousin, Julian the Apostate. Julian had only avoided the earlier purge of his family because he was too young to pose a threat. But the young grow up. Julian received a Christian education and was trained for a position in church leadership. But he harbored and nurtured a secret hatred for the religion of the court, a religion under which his family was all but exterminated. He studied the banned texts of Eastern mystics & Greek philosophers; all the more thrilling because they were forbidden. Julian became so immersed in paganism, he was made the leader of a secret order devoted to keeping the ancient religion alive.
Despite his hostility toward Christianity, Julian recognized the Faith was too deeply entrenched in the Empire to turn back the sundial to a time when Christians were persona non grata. He decided instead to simply pry loose the influence they’d established in the civil realm. He appointed non-Christians to important posts & reclaimed some of the old pagan temples that had been turned into churches back to their original use.
Julian enacted a policy of religious tolerance. Everyone was free to practice whatever faith they wanted. Make no mistake, Julian wanted to eliminate Christianity. He felt the best way to accomplish that, wasn’t by attacking it outright. After all, 200 years of persecution had already shown that wasn’t effective. Rather, Julian figured all the various sects of Christianity would end up going to war with one another and the movement would die the death of a thousand cuts, all self-inflicted. His plan didn’t work out, of course, but it was an astute observation of how factious the followers of Christ can be.
When Julian was killed in 363 in an ill-advised war against the Sassanids, the pagan revival he’d hoped for fizzled. The reasons for its demise were many. Because Paganism is an amalgam of various often contradictory beliefs and worldviews it lacked the cohesion needed to stare down Christianity. And compared to the virtuous morality and ethical priorities of Christianity, paganism paled.
Julian’s hoped-for elimination of Christianity by allowing its various sects to operate side by side never materialized. On the contrary, major advances were made toward a mutual understanding of the doctrinal debates that divided them. The old Athanasius was still around and as an elder statesman for the Church he’d mellowed, making him a rallying point for different groups. He called a gathering of church leaders in Alexandria in 362, right in the middle of Julian’s reign, to recognize the Creed of Nicea as the Church’s official creedal statement. His resolution passed.
But trouble was brewing in the important city of Antioch. While the Western churches under the leadership of the Bishop of Rome remained steadfast in their loyalty to the Nicean Creed, the Eastern Empire leaned toward Arianism. Antioch in Syria was a key Eastern city split between adherents of Nicea & Arianism. The official church, that is, the one recognized by the Emperor in Constantinople had an Arian bishop. The Nicean Christians were led by Bishop Paulinus in a separate fellowship. But in 360, a new bishop rose to lead the Arian church at Antioch – and he was a devoted Nicean named Meletius! This occurred right at a time when more & more Eastern bishops were coming out in favor of the Nicene Creed. These Eastern bishops supported Meletius and the New Niceans of Antioch. We might think this would see a merger of the old-Niceans under Paulinus with the new, and à we’d assume wrongly. Rome & the Western church considered Paulinus the rightful bishop of Antioch & remained suspicious of Meletius & the new-Niceans. Efforts on their part to negotiate with & be accepted by the Western church were rebuffed. This served to increase the divide between East & West that had already been brewing for the last few decades.
A new center of spiritual weight developed at this time in Cappadocia in central-eastern Asia Minor. It formed around the careers of 3 able church leaders, Basil the Great, his brother Gregory of Nyssa, and their friend, Gregory of Nazianzus. Their work answered the lingering concerns that hovered around the words the Nicaean Council had chosen to describe Jesus as being of the same substance as the Father. These 3 Cappadocian Fathers were able to convince their Eastern brothers that the Nicean Creed was the best formulation they were likely to produce and to accept that Jesus was of the same substance as the Father, and so God, not a similar substance and so something other than or less than God, as the Arians held it. They pressed in on terms that made it clear there was only one God but 3 persons who individually are, and together comprise that one God; The Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. They said the 3 operated inseparably, none ever acting independently of the others. Every divine action begins from the Father, proceeds thru the Son, and is completed in the Holy Spirit.
In 381 at the Council of Constantinople, the Eastern Church demonstrated its acceptance of the Cappadocian Fathers’ theology by affirming their adherence to the Nicean Creed. This effectively marked the end of Arianism within the Empire. And unlike the previous 3 ecumenical councils, the Council of Constantinople was not followed by years of bitter strife. What the council failed to do was resolve the split in the church at Antioch. The West continued to support the Old-Niceans while the East supported the New. It was clear to all tension was building between the old seat of Imperial power & the new capital; between Rome & Constantinople. Which church & bishop would be the recognized leader of the whole? Antioch became the site where that contest was lived out thru their surrogates, Paulinus & Meletius.
The Council of Constantinople attempted to deal with this contest by developing a system for how the churches would be led. The rulings of the Council, and all the church councils held during these years are called Canon Law, which established policy by which the Church would operate. One of the rulings of the Council of Constantinople established what was known as dioceses. A diocese was a group of provinces that became a region over which a bishop presided. The rule was that one diocese could not interfere in the workings of another. Each was to be autonomous.
Though Jovian followed Julian as emperor in 363 his reign was short. He followed a policy of religious toleration, as did Valentinian I who succeeded him. Valentinian recognized the Empire was too vast for one man to rule & appointed his younger brother Valens to rule the East. Valens was less tolerant than his brother & attacked both paganism & the Nicean Christians. But Valens was the last Arian to rule in either East or West. All subsequent emperors were Orthodox; that is, they followed the Nicean Creed.
When Valentinian died in 375, rule of the Western Empire fell to his son Gratian. When Valens died, Gratian chose an experienced soldier named Theodosius to rule the East.
Gratian & Theodosius presided over the final demise of paganism. Both men strongly supported the Orthodox faith, and at the urging of Bishop Ambrose of Milan, they enacted policies that brought an end to pagan-worship. Of course, individuals scattered throughout the Empire continued to secretly offer sacrifices to idols & went through the superstitious rituals of the past, but as a social institution with temples & a priesthood, paganism was eradicated. Under the reign of Theodosius, Christianity was made the official religion of the Empire.
We’ll end this episode with a look at how the church at Rome emerged during the 4th & 5th Centuries to become the lead church in the Empire.
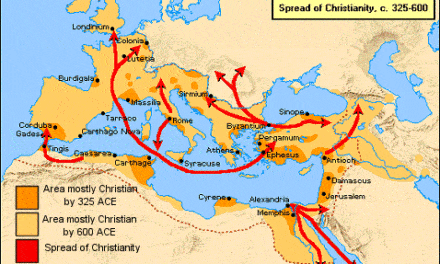
In theory all the bishops of the Empire’s many churches were equal. In reality, from the time of the Apostolic Fathers, some gained greater prominence because their churches were in more important cities. During the 2nd & early 3rd Centuries Alexandria, Antioch, Rome & Carthage were the places of the greatest spiritual gravity; their senior pastors recognized as leaders, not just of their churches but of The Church. The Council of Nicaea in 325 recognized Alexandria as the lead church for all North Africa, Antioch in the East & Rome as preeminent in the West.
Constantinople, the new Eastern political capital, was added to that list in 381 by the Council of Constantinople. As one of its rulings in canon law, the Council declared Constantinople 2nd only to Rome in terms of primacy in deciding church matters.
We might assume the Bishop of Rome would gladly accept this finding of the Council, being that it acknowledged the Roman “see” (that is, a bishop’s realm of authority) as primary. He didn’t! He objected because the Council’s ruling implied the position of a Church and its Bishop depended on the status of their city in the Empire. In other words, it was the nearness to the center of political power that weighed most. The Bishop of Rome maintained that the preeminence of Rome wasn’t dependent on political proximity but on historical precedent. He said the decree of a Synod or Council didn’t convey primacy. The Roman Bishop claimed Rome was primary because God had made it so. At a Council in Rome a year after the Council of Constantinople, the Roman Bishop Damasus said Rome’s primacy rested on the Apostle Peter’s founding of the Roman church. Ever since the mid-3rd C, Roman Christians had used Matthew 16, Luke 22 & John 21 to claim their church possessed a unique authority over other churches & bishops. This Petrine Theory as it’s come to be known was generally accepted by the end of the 6th C. It claimed Peter had been given primacy over his fellow apostles, and his superior position had been passed on from him to his successors, the bishops of Rome, by apostolic succession.
In truth, there was already a substantial church community in Rome when Peter arrived in Rome and was martyred. The Christians honored Peter as they did all their martyrs by making his grave a popular gathering place. Eventually, it became a shrine. Then, when persecution ended, the shrine became a church. The leader of that church became associated with Peter whose grave was its central feature.
When Constantine came to power, he ordered a basilica built on the site on Vatican Hill. To mark that a new day of favor toward the Church had come, Constantine gave the Lateran Palace where the Roman Empress had lived to the Bishop of Rome as his residence. But the story that arose later which puts Emperor Constantine on his face before Sylvester, the Bishop of Rome, pleading forgiveness in sackcloth & ashes & handing over to him the rule of Italy & Rome, is a fiction.
Until Bishop Damasus in the mid-4th C, the Roman bishops were competent leaders of the church but tended toward weakness when dealing with the Emperors, who often sought to dominate the Faith. A dramatic change occurred at the end of the 4th C, when under Ambrose of Milan, the Church dictated to the Emperor.
Bishop Damasus, a contemporary of Ambrose, installed the Primacy of Peter as a central part of Church doctrine. He claimed the Roman church was started by Peter, who’d passed on his authority to the next bishop, who’d, in turn, handed it to his successor and that each Bishop of Rome was a recipient of Peter’s apostolic authority. Since Peter was the leader of the Apostles that meant the Roman church was the lead church and the Bishop the leader, not just of Rome but of all Christendom. Damasus was the first to address other bishops as ‘sons’ rather than ‘brothers.’
Historical events during the 4th & 5th Centuries enhanced the power of the Bishop of Rome. When Constantine moved the political capital to Constantinople in 330, it left the Roman Bishop as the strongest individual in Rome for long stretches of time. People in the west looked to him for temporal as well as spiritual leadership when a crisis arose. Constantinople & the Emperor were hundreds of miles & weeks away; the Roman bishop was near; so people turned to him to exercise authority in meeting political as well as spiritual crises. In 410 when Alaric and the Visigoths sacked Rome, Bishop Innocent I used clever diplomacy to save the city from the torch. When the Western Empire finally fell in 476, the people of Italy looked to the Roman Bishop for civil as well as religious leadership.
Great leaders like Cyprian, Tertullian, & Augustine were outstanding men of the Western church who counted themselves as being under the leadership of the Bishop of Rome. The Western Empire had also managed to stay free of the heretical challenges that had wracked the East, most notably, the brouhaha with Arius and his followers. This doctrinal solidarity was due in large part to the steadfast leadership of Rome’s Bishops.
Another factor that contributed to Rome’s rise to dominance was the decline of the other great centers. Jerusalem lost its place due to the Bar Kochba rebellion of the 2nd C. Alexandria & Antioch were overrun by the Muslims in the 6th & 7th Centuries; leaving Constantinople & Rome as the centers of power.
In an Imperial edict in AD 445, the Emperor Valentinian III recognized the supremacy of the Bishop of Rome in spiritual affairs. What he enacted became Canon law for all.
Another great boon to the influence & prestige of the Roman Bishop was the missionary work of monks loyal to Rome. Clovis & Augustine planted churches in northern France & Britain, all owing allegiance to Rome.
But above all, the Roman church was led by several able bishops during this time; men who overlooked no opportunity to enhance & extend their power.
Leo I was bishop at Rome from 440 to 461 & by far the ablest occupant of the Bishop’s seat until Gregory I, 150 years later. His skill earned him the title “Leo the Great.”
We’re not sure when Rome’s bishops began to be called “pope”, a title which for years had been used by the bishop of Alexandria. But Leo was the first to refer consistently to himself as pope – from Latin, a child’s affectionate term for papa. In 452, Leo persuaded Attila the Hun to let the city of Rome alone. Then 3 years later when the Vandals came to sack the city, Leo convinced them to limit their loot-fest to 2-weeks. The Vandal Leader Gaiseric kept his word, and the Romans forever after esteemed Leo as the one who saved their city from destruction.
Pope Leo insisted all church courts & the rulings of all bishops had to be submitted to him for final decision. This is what Valentinians III’s edict of 445 granted and he was determined to apply it.
Pope Gelasius I, who ruled from 492 to 496, said that God gave sacred power to the Pope and royal power to the King. But because the Pope had to account to God for the King at the judgment, the sacred power of the Pope was more important than royal power. So, civil rulers should submit to the Pope. While the emperors didn’t all automatically knuckle under to popes, most did resign a large part of authority & political influence to the Roman Bishops.





Great help in understanding the development of the concept of the pope.