This episode of Communio Sanctorum is titled, “Breaking Up Is Hard to Do.”
In our study of the History of the Church, we get to examine some periods when the followers of Jesus did some amazing, God-honoring, Christ-exalting, people-blessing things. In future episodes, we’ll take a longer look at how the Gospel has impacted history and world civilization for the better.
But, we have to be honest and admit there have been too many times when the Church totally fumbled the ball. Worse than that, after fumbling, they stepped on and kicked it out of bounds!
The danger I face as we deal with these atrocious moments in Church History is of being assumed to be hostile to the Body of Christ. When I speak about the abysmal career of some of the popes, some listeners assume I’m Catholic-bashing. Later, when we get to the Reformation era and take a look at some of the Reformers, I’ll be accused of being a closet-Catholic!
So I want to pause here and say à This isn’t a podcast about me, but I need to use me as an example . . .
As most of you know, I’m a non-denominational Evangelical pastor. I’m not a scholar, not even close. I’m just a guy who loves history and decided to share what he was learning about the history of the church with others because at the time CS began, there just wasn’t a short-format church history podcast available. While I genuinely try to be unbiased in presenting the story of the Church, it’s inevitable I’ll slant the narrative at points. I’ve already made it clear that when I do offer mere opinion, I’ll preface it with a warning, but infrequent side comments can still color the material. Even what adjectives I pick reveal bias.
While I aim to be faithful in my own walk with God, my role in my family as a husband and father, and my calling as a pastor, I freely admit I’m still a man in process. I have many faults and a long way to go to be conformed to Christ’s image. Keenly aware of how far I have to go is what causes me to wonder how God could use me! Yet use me He does, week after week, in my role as pastor. I’m such a flawed vessel, yet God keeps pouring His grace thru me. It’s humbling.
The point is this: While so much of Church History is flat-out embarrassing, God still uses the Church, still works by His Spirit through His people to accomplish His purposes. So when we see the Church stumble, regardless of what group it is, what era, what label is applied to those who mess up, let’s not white-wash, edit, or redact. Let’s tell it like it is; own it as part of our history, but remember that while man fails, God never does.
From the late 9th to 10th C the position of Roman bishop once held by such godly men as Popes Leo and Gregory was turned over to a parade of corrupt nobles who were anything but.
This was a time when the position of the pope was a plum political appointment, with the potential of gaining great wealth and power for the pope’s family. The intrigue surrounding the selection of the pope was vast and nefarious. An Italian heiress named Marozia [mah-RO-zee-ah], controlled the bishop’s seat at Rome for 60 years. She was one bishop’s mother, another’s murderer and a third’s mistress. In what just about everyone recognizes as a low point for the Papacy, Octavianus, Marozia’s grandson, celebrated his impending election as Pope John XII, by toasting the devil. Once in office, his behavior was far from saintly. The immorality that attended his term was legendary. Corruption of the office didn’t end with his death. Reform was desperately needed and many called for it. But one man’s reform is another’s loss of power and access to wealth.
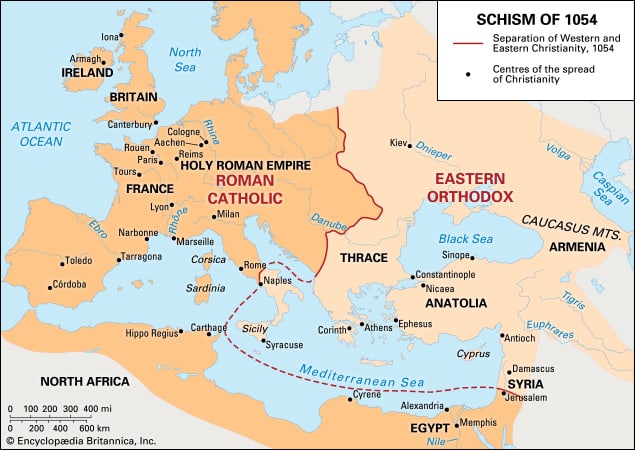
Though the Western and Eastern halves of the Church had quarreled for centuries over minor doctrinal issues and who ought to lead the Church, they still saw themselves as one Body. That unity was doomed by many years of contention and the fragmenting of the world into conflicted regions brought about by the dissolving of the Roman Empire and constant invasion of outsiders. The emergence of Islam in the 7th C accelerated the break between East and West. We might assume the 2 halves of the old Empire would unite in face of the Islamic threat, and there were times when that seemed hopeful. But the reality was, Islam presented a threat across such a huge front, the various regions of Christendom ended up having to face the threat on their own.
Between the 9th and 13th Cs, three separate challenges split Christianity into 2 disparate camps. Like taps on a diamond, each furthered the emerging rift until finally the break came.
The first tap had to do with the Nicene Creed hammered out at the Council of Nicea all the way back in the early 4th C when Constantine was Emperor. In the 9th C, the Nicene Creed still stood as the standard formulation for how Christians in the East and West understood God. But the Spanish church added something they thought would make the creed clearer. The original creed stated, “The Holy Spirit proceeds from the Father.” The revised creed of the Spanish church said, “The Holy Spirit proceeds from the Father and the Son.”
This reflected the work on the Trinity that had been conducted by later Councils. Remember, the very first councils were consumed with understanding the nature of Jesus and settled on the doctrine He is both fully God and fully Man. They labored hard to find just the right words to say that. Then, they turned their attention to the issue of the Trinity, and after much labor settled on the wording that God is one in essence but three in person. For most people, that was enough, but theologians have minds that want to go further. They debated over how to understand the divinity of God. Who actually possessed deity; all three equally? Or did one possess it, then shared it with the others?
The Western Church centered held the idea divinity was co-equal and underived in Father, Son and Holy Spirit. But relationally the Son proceeds from the Father, and the Holy Spirit then proceeds from both Father and Son. This seemed to accurately reflect the subordinate missions assigned the 2nd and 3rd members of the Trinity in the Bible.
The Western Church adopted the revised Nicene Creed. The Eastern Church balked! Everyone agreed the Nicene Creed had been a work of the Spirit of God illuminating the minds of the Council to the Word of God. It was inviolable! How could Rome think to fiddle with it? And especially without consulting them? Why, at the Councils of Ephesus and Chalcedon, the Bishops committed themselves never to change the creed.
According to Eastern theologians, divinity dwelt only in the Father. The Father then shared the divine being with the Son and Spirit. They could not say the Spirit “proceeds from the Father and the Son.” If the Spirit arose from “the Father and the Son,” the Son would possess divine being co-equally with the Father.
While there had been potential doctrinal rifts before, the East and West had always been able to reach a consensus. That historic consensus became increasingly distant as this debate, known as the Filioque Controversy, raged. Filioque is Latin for “and the Son.”
In 867 Photius, bishop of Constantinople formally denounced the added phrase. Five years later, Pope Adrian II offered to drop the phrase “and the Son” from the Nicene Creed. Rome would drop the Filioque clause if the Eastern church accepted the Pope’s supremacy over the Church. Photius declined. >> Tap 1.
Get ready for Tap 2 …
One day in AD 1048, three shoeless pilgrims—Bruno, Humbert, and Hildebrand walked together through the gates of Rome. Each in his own way would transform the Roman church.
Bruno was elected Pope Leo IX. He immediately set about reforming the Roman church morally and theologically. To keep priests from passing ecclesiastical positions to their children, he demanded celibacy. Next, he moved to extricate the Church from secular entanglements and obligations to European nobility. Bruno and his successor popes really believed God had given them authority over all Christians.
The new bishop of Constantinople, Michael Cerularius, refused to recognize Bruno as Pope. He closed every church in Constantinople loyal to Rome. Bruno then sent envoys to Constantinople to negotiate peace. His chief envoy was his friend Humbert. Before leaving Rome, Humbert wrote a bold notice in the Pope’s name. This official church notice is called a bull. We get our word “bulletin” from it. A Bull was an authoritative announcement of intention to follow a particular course. It’s based in the authority of the person who writes it or whose name it bears.
Humbert made the journey from Rome to Constantinople, bull in hand. He arrived on July 16, 1054, marched into the Hagia Sophia while Communion was being observed. As one author says, Humbert’s notice was a lot like a Texas longhorn: It had a point here, a point there, and a lot of bull in between. Condemned in the bull were the Eastern practices of allowing priests to marry, refusing to recognize baptism performed in Roman churches, and deleting the Filioque.
For the record, the Roman church had allowed priests to marry for several centuries, the Eastern church did not refuse to recognize Roman baptism, and they absolutely did NOT DELETE the phrase” and the son” from the Creed – The Western Church had added it!
Humbert threw the bull on the Communion table, turned his back on the priest, and walked out, knocking the dust from his sandals and yelling “Let God judge!” A deacon picked up the bull and chased after Humbert, begging him to take it back. Humbert refused.
The Papal Bull was viewed by the Eastern Church as the proverbial gauntlet, thrown at their feet by the Pope. The options seemed clear; either submit to the Pope’s undisputed authority over the Church, or be considered by Rome a breakaway church.
Tap 2
The third and decisive tap that sundered East from West was the Crusades, specifically, the 4th. I need to make clear we’re only dipping a toe into the subject of the Crusades for now. They’re a major part of Church History we’ll spend a lot more time on in future episodes. For now, we’re only looking at how the Crusades served to split the Western and Eastern Churches.
But even before THAT, I’m compelled to remind everyone that when I refer to the Eastern Church, what I really mean is the Greek Orthodox or Byzantine Church; not the Church of the East we’ve looked at in earlier podcasts. For simplicity sake. Picture a map of the ancient world; that swath of the globe that includes to the far left, Spain and Northwest Africa, up thru England and Scotland. Now, put the Middle East with Mesopotamia in the center of that mental map, and at the far right, China and Japan.
Now, draw a mental oval over Spain, the British Isles, France, Germany, Italy, Scandinavia; shade it blue – That’s the Western Church, speaking Latin, and centered at Rome under the Popes.
Next, draw another oval over all East Europe and West Asia; shade it Green – That’s the Byzantine Church, speaking Greek and centered at Constantinople under the Patriarchs.
Finally, draw a 3rd oval over The Middle East, Mesopotamia, Persia, Central Asia, India, China and all the way to Japan. Shade it red – That’s the Nestorian Church of the East, that speaks mainly Syriac and is headquartered at Nisibis & Edessa under the leadership of the Metropolitans.
Note how much larger that 3rd sphere is. It covers a territory and population much larger than the two to its west combined. Yet in the popular review of Church History, this Church of the East is often neglected. The reason for that neglect is a subject for a later episode.
My point here is that when we speak of the break between the Eastern and Western Churches, let’s be sure we understand that the description of the Byzantine Church as the Eastern Church isn’t really accurate. It’s only a description of the Byzantine Church as being to the geographic East of the Western, Latin Church.
Now, back to our look at the 3rd tap that severed West from East . . .
As we’ve seen in previous episodes, penance played a major role in the religious life of Medieval Christians. Many believed they could prove themselves worthy of God’s favor by going on a “pilgrimage.” So pilgrims traveled to shrines containing the bones of saints and relics from the Biblical story. European cathedrals were centers where these sacred items were kept. But the greatest pilgrimage of all, one taken by not a few sincere believers was to Jerusalem. Even today with modern forms of transportation, a trip to Israel is a major event requiring special arrangements and a significant investment. Imagine what it meant for a pilgrim of the 10th or 11th C! They walked hundreds of miles, braved a risky voyage aboard a ship that traveled through stormy, pirate-infested seas. This was no Disneyland ride; there were real-deal pirates who’d slit your throat or sell you into slavery. Fun stuff.
Pilgrimages became such a fixture of medieval society, to impede a pilgrim’s journey was thought to imperil his/her salvation. So a whole trade developed in assisting pilgrims reaching their destination, whether it was some cathedral or holy shrine in Europe, or the great pilgrimage to the Holy Land.
From AD 638, Muslims controlled Jerusalem and the routes leading there. They required pilgrims to pay special fees. So in 1095 in France, Pope Urban II responded by preaching one of history’s most influential sermons. We’ll go into the details later. For now, just know he said, “Your Eastern brothers have asked for your help! Turks and Arabs have conquered their territories. I or, rather, the Lord begs you … destroy that vile race from your brothers’ lands!”
The response astounded both the Pope and Europe’s nobility. The crowd of commoners began to chant, “Deus vult = God wills it!” There was an immediate response of hundreds to go in relief of their imperiled brothers. As the days passed, the fervor spread and soon, nobles and serfs set off on the Great Pilgrimage to liberate Jerusalem from the infidels. They sewed crosses onto their tunics and painted them on their shields. Nobles forged new swords and spears while commoners grabbed whatever might make for a weapon and set off. They agreed to gather in Constantinople. The First Crusade was off and running.
Among the peasants that set out on the 1st Crusade was a large group who followed a monk known as Peter the Hermit. The swarthy monk had not bathed in decades. He rode a burro that, according to some bore a remarkable resemblance to its rider. Peter’s preaching was even more powerful than his odor. In 9 months, he gathered 20,000 European peasants to fight the Eastern infidel. They caused immediate chaos when they arrived in Constantinople. Complaints of robbery poured into the Emperor’s office. He knew the untrained peasants were no match for the Muslims who cut their teeth on conquest, but he couldn’t let them linger in his city. So he ferried them across the river where they began pillaging the homes of Eastern Christians, straining relations between the Byzantine and Roman churches. 2 months later, these peasants marched straight into an ambush. Peter, still in Constantinople begging for supplies, was the lone survivor. He joined another army, led by European nobility. These Crusaders clashed with the Muslims in Antioch, then continued on to Jerusalem.
On July 15, 1099, Jerusalem fell to the Crusaders. Near the Temple Mount, the blood flowed ankle-deep. Newborns were thrown against walls. Crusaders torched a synagogue and burned the Jews inside alive. To this day, this wholesale slaughter affects how Jews and Muslims perceive the Church.
A couple more Crusader campaigns were launched, then in 1198 a noble became Pope Innocent III. He inspired the 4th Crusade that would finally divide the Byzantine and Roman Churches.
The bottom line of the 4th Crusade is that it was more than anything, a commercial venture. The merchants of the powerful city-state of Venice agreed to supply the Crusaders with ships at the cost of 84,000 silver coins. They were then to sail to Egypt and destroy a key Muslim base that would open up trade. In the summer of 1202, the Crusaders arrived in Venice expecting to sail to Egypt. But there was a problem: Only one-third of the expected number of Crusaders showed up, and they came up with only 50,000 silver coins.
Not to worry, an ambitious Eastern prince who fancied himself someone who deserved a fate and station better than the one life had dealt him, offered to finance the crusade à get this: Under the condition the Crusaders sail to Constantinople FIRST and dethrone the current Emperor. Once that was done, they could be on their merry way. Pope Innocent III forbade the assault on Constantinople, but no one paid him any mind. On July 5, 1203, the Crusaders arrived in Constantinople. But the people of the city were quite over the mess these Europeans kept making of things and revolted. They pre-empted the Crusaders attempt to install their own emperor and instead selected a fiercely anti-Crusader ruler.
The Crusaders were furious. They’d set out to destroy Muslims in Egypt and saw their side trip to Constantinople as a brief diversion. Now, they were stranded in the Eastern Capital. With the promise of plunder the motive for their venture in the first place, they decided to go to town on those they now deemed their enemies – the people and city of Constantinople. One priest promised the Crusaders if they died in the now “holy cause” of sacking the city, they had the Pope’s blessing and would go immediately to heaven. The Pope had said no such thing; on the contrary, he’d forbidden the entire campaign. But people hear what they want, and the Crusaders took that priest’s announcement as a license to do whatever they pleased.
On Good Friday, 1204, with red crosses on their tunics, the Crusaders sacked Constantinople. For 3 days, they raped and killed fellow believers. The city’s statues were hacked to pieces and melted down. The Hagia Sophia was stripped of its treasures. A harlot performed sensual dances on the Lord’s Table, singing vile drinking songs. One writer lamented that the Muslims were more merciful than those who bore a cross on their garments.
Neither the Byzantine Empire nor Church recovered from those 3 horrible days. The Crusaders ruled the Eastern Empire for the next 60 years. The Eastern emperor set up a new capital in nearby Nicaea, to which many of the people of Constantinople fled. They remained there until 1261, when an Eastern ruler retook the City.
Pope Innocent III tried to prevent the fall of Constantinople, but no one had listened. Afterward, he attempted to reunite the churches, but it was too late. After the 4th Crusade, the Church was shattered into 2 communions. Today we know them as the Roman Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches.
And while there have been a few attempts to affect a reconciliation recently, the wight of history has served to keep them at odds.





Thank you, again, so very much, for this “labor of love” podcast! Words can’t express how much it means to me to have this available. I’ve always wanted to delve into church history, but have had neither the time nor the resources to pursue such an endeavor. Thank you, thank you, THANK YOU!!!
I also want to thank you for the preface to this podcast. The humility with which you approach these pod casts are incredibly refreshing. Perhaps we cannot avoid our particular biases (in any matters) completely; but, frankly, I’ll take your kind of bias any day!! Which leads me to my next expression of gratitude: thank you for “keeping it real.” I’ve never been one who cares much (at all) for “church bashers” (especially the ones from within the church); but nor do I care for those who “white wash” over the horrible things we, as a group, have committed. My heart breaks as I listen to some of the history presented here, but I wouldn’t have it any other way. The TRUTH will set us free (slightly out of context, but you get what I mean).
I understand that you are a busy man, who must attend to his family, church, and calling, and I wouldn’t have it any other way. But I want you to know that we who faithfully follow Communio Sanctorum are EXTREMELY GRATEFUL for the loving sacrifice you give in providing this. May the blessing of Father God overwhelm you in all that you set your heart and hands to do, for His glory!!!
Lemuel,
I wish I had the words to express my appreciation for your post. Since I don’t, I’ll just have to say “Thank you.”
But please know that as you read those words, my heart aches to be able to give you a big, brotherly hug, for you have blessed me greatly today.
Lance
You are most welcome! Meant every word of it. All I ask is that (in time) you “just keep those cards and pod casts coming!” 😉
I heartily agree with Mr. Dees! Your humility is truly inspiring Pastor and an example to all. I add my own thanks for your labor of love. I eagerly anticipate each episode, and often listen more than once.
Thank you Samuel.